The world of search engine optimization (SEO) is complex and always growing. There’s a lot to consider when optimizing your website for better search engine rankings and increased organic traffic.
To help you with the basics, we’ve put together this checklist of SEO best practices. We’ll mostly focus on on-page SEO, but read to the end for a few tips on off-page and technical SEO as well.
Here are eleven tips on search engine optimization (SEO) best practices to improve your on-page optimization efforts.
- Keyword research
- Title tags
- Meta descriptions
- Targeted and unique content
- Relevant URL
- Headings
- Internal page linking
- Image alt text and filenames
- Readable content
- Schema markup
- Monitor your performance
But before we go over our on-page checklist, let’s quickly review the SEO basics.
SEO fundamentals: what to know
Search engine optimization is all about improving and optimizing a page or website to increase visibility in search engines, such as Google or Bing. When you optimize for SEO, you’re making it easier for people to find your website as well as the product, service or information you offer.
The goal of SEO strategy is to boost your presence in search results, attracting more visitors to your site and increasing conversions.
There are a few types of SEO that contribute to how a site or page ranks on Google search and other search engines. These include technical SEO, off-page SEO and on-page SEO. A holistic SEO strategy addresses all three areas to achieve the best results.
- On-page SEO: This involves optimizing the content and HTML source code of a page. It’s everything you have direct control over on your website, including the text, images, headings, title tags, and more. This guide will focus primarily on these factors.
- Off-page SEO: This refers to actions taken outside of your own website to impact your rankings. An important off-site SEO factor is earning backlinks from other reputable sites.
- Technical SEO: This focuses on improving the technical aspects of a website to help search engines crawl and index it more effectively. It includes things like site speed, mobile-friendliness, and creating an XML sitemap.
In this guide, we’re primarily focusing on on-page SEO. There is a host of information on SEO and content marketing on the Orbit Blog if you’re interested in learning more about the other types of SEO.
Now, on to the on-page SEO best practices checklist.
1. Start with keyword research
If improving search engine ranking performance is the goal, keyword research should be one of your very first steps. Keyword research is the process of finding and analyzing the terms people use in search engines. The goal is to find keywords that have a good search volume, are relevant to your business, and have a manageable level of competition.
First, you need to consider: What is your audience searching for? What terms, phrases and questions do you want to rank for?
Start by brainstorming core topics related to your business. Then, use SEO tools (like Moz, Semrush, Ahrefs, etc.) to find specific keywords related to those topics. Look for a mix of short-tail keywords (e.g., “web design”) and long-tail keywords (e.g., “how much does a small business website cost”).
Long-tail keywords usually have a lower search volume, but they are often less competitive and attract more qualified traffic. Analyze the search intent behind these keywords– are users looking to buy something, find information, or locate a specific website? Aligning your content with this intent is critical.
Best practices:
- Search google for any keywords you’re thinking of targeting- do the search results match the content you’re writing? Does the intent match?
- Compare your domain and page authority to the keyword difficulty. Aim to target keywords with a difficulty lower than your authority score.
- Incorporate semantic keyphrases and content. This will help signal that your article is relevant for the topic, and may be more useful to users.
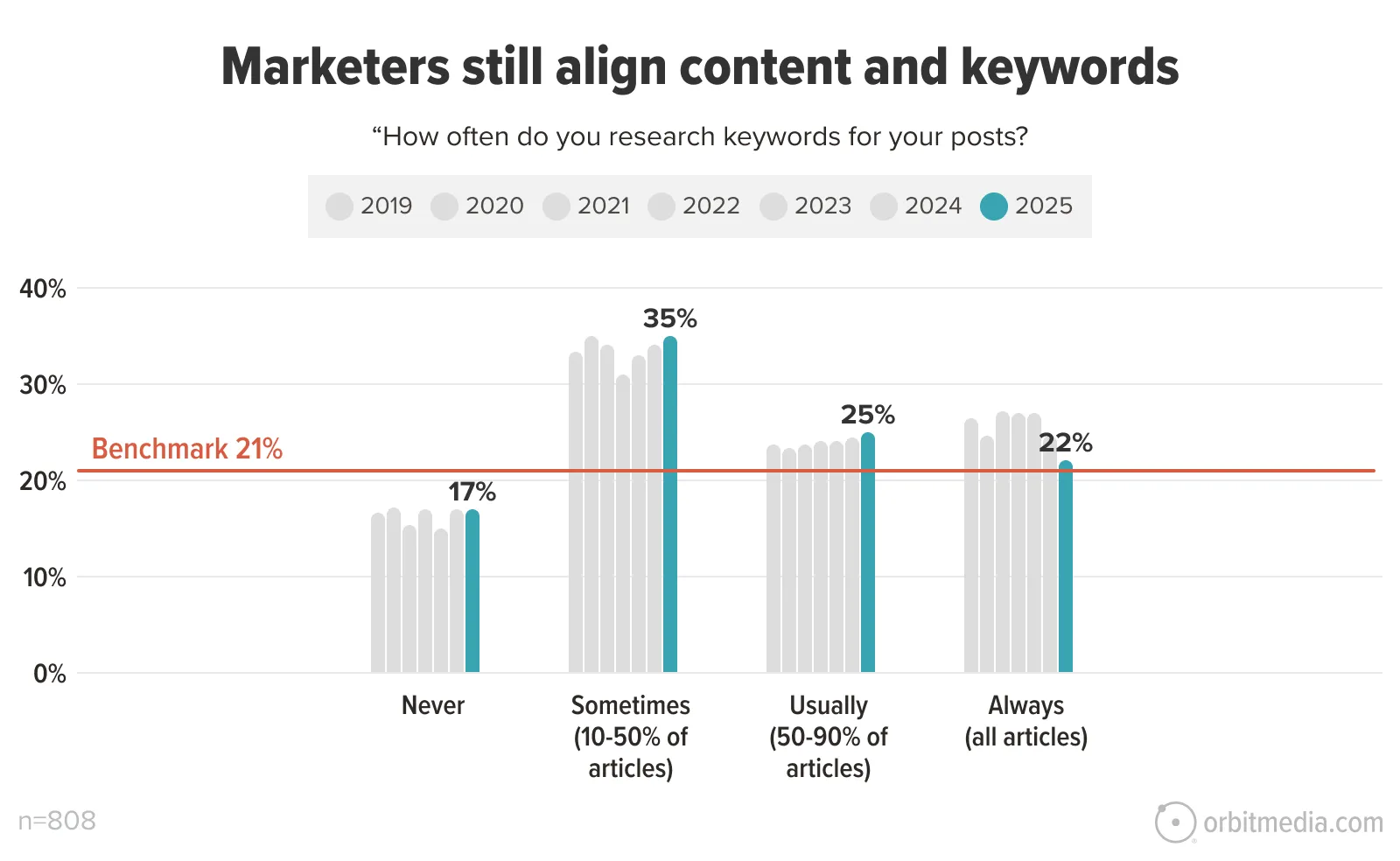
Our most recent blogger survey found that most marketers research keywords for their posts.
2. Title tags
Aside from conducting (and using) keyword research for your content, the title tag is one of the most important on-page SEO factors. (If you need some pointers, here is a step-by-step guide on how to research keywords.)
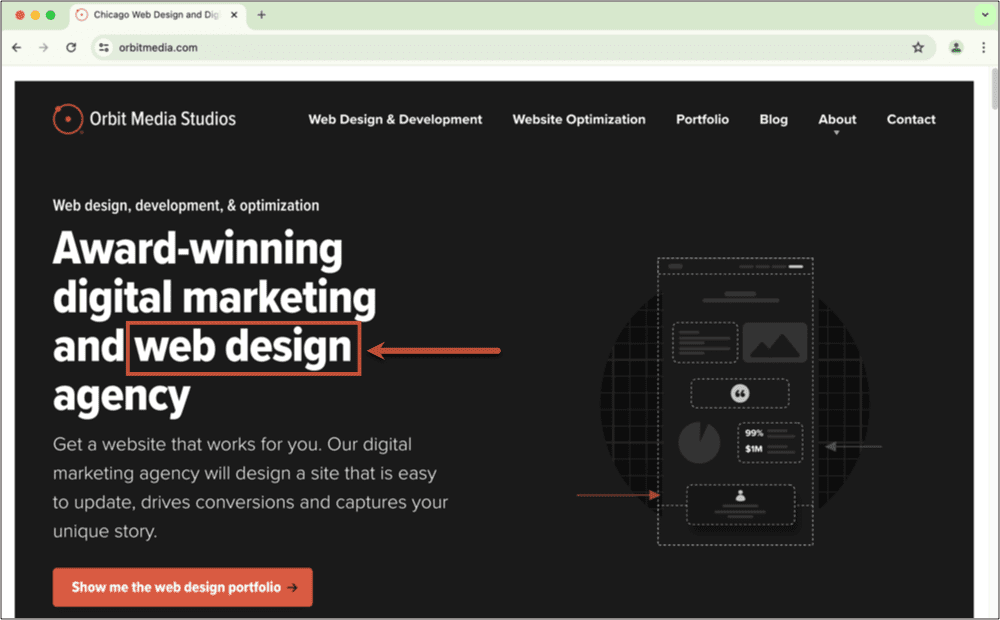
The title tag should be the keyphrase or keyword you are trying to rank for, as well as the topic of the page content. Search engines use title tags to get an idea of what a page is about, so they can display and highlight relevant content in search results. Title tags also signal to the people reading the content what they can expect to find when clicking on a search result. Accurate title tags that are written with relevant keywords and search intent in mind increase visibility and click-through rate.
Let’s say you’re trying to rank for “Chicago Web Design,” your title tag may look like this:
Chicago Web Design and Development | Orbit Media
Best practices:
- Your title tag should be written like this: Primary Keyword – Secondary Keyword | Brand Name.
- Use a dash in between your keyword phrases and a pipe at the end before your brand name.
- Make your title tags unique and accurate, don’t duplicate title tags.
- Don’t forget to write for humans- keep it simple, and try to grab the reader’s attention.
- Keep title tags at 55 characters or less in length, including spaces. If you’re interested in learning more about the new title tag guidelines, check out this post by Dr. Pete.
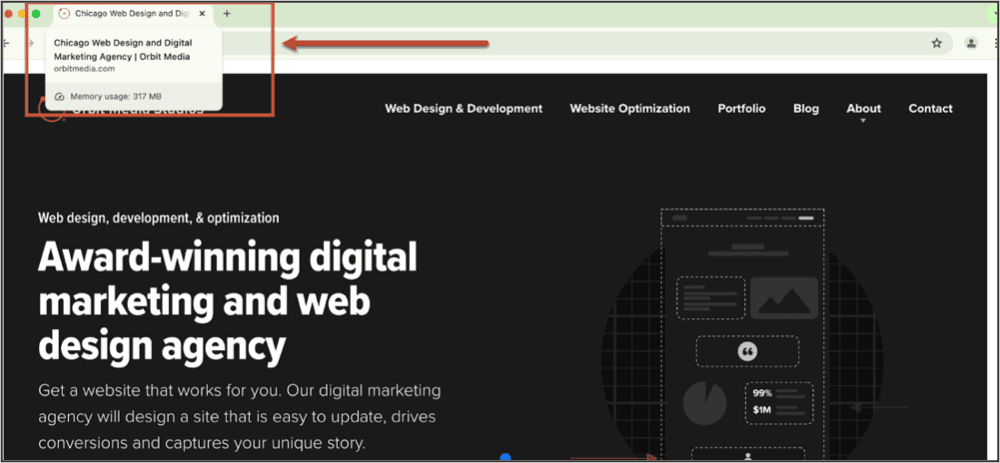
Example of a title tag in a browser:
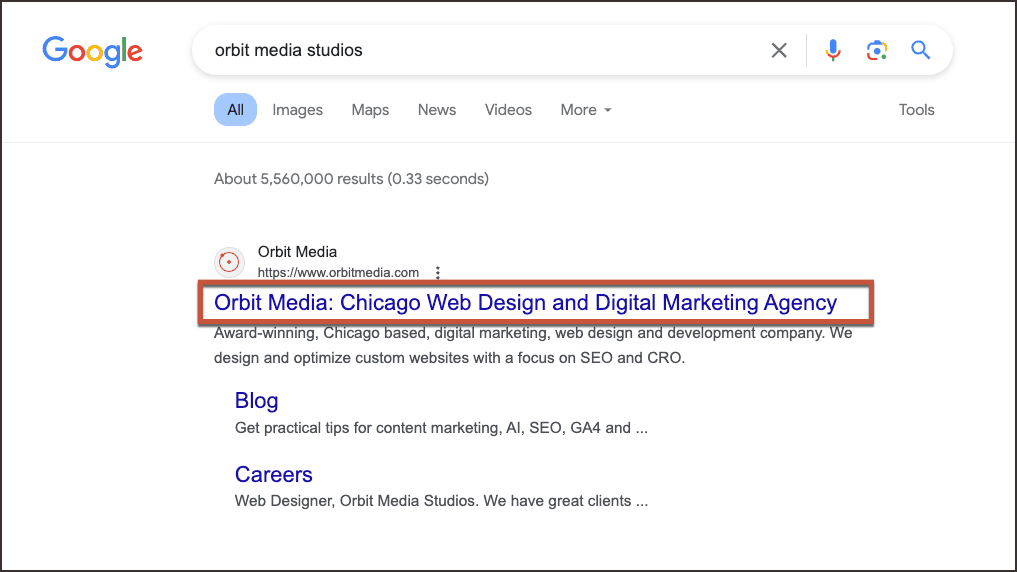
Example of a title tag in search engine results:
3. Meta descriptions
Meta descriptions, while not as important in search engine rankings, are extremely important in getting users to click through from the search engine results page (SERP) to your website. Meta descriptions should use keywords wisely, but more importantly, they should include a compelling description that grabs the user’s attention and encourages them to click.
Much like title tags, the SERPs will highlight keywords the user searched for, increasing the likelihood of the user clicking through to your website.
Best practices:
- Write a compelling meta description that will encourage the user to click.
- Stay within 150 to 160 characters.
- Avoid duplicate meta-descriptions.
- Do not use quotes or any non-alpha characters (Google cuts them out of the meta description).
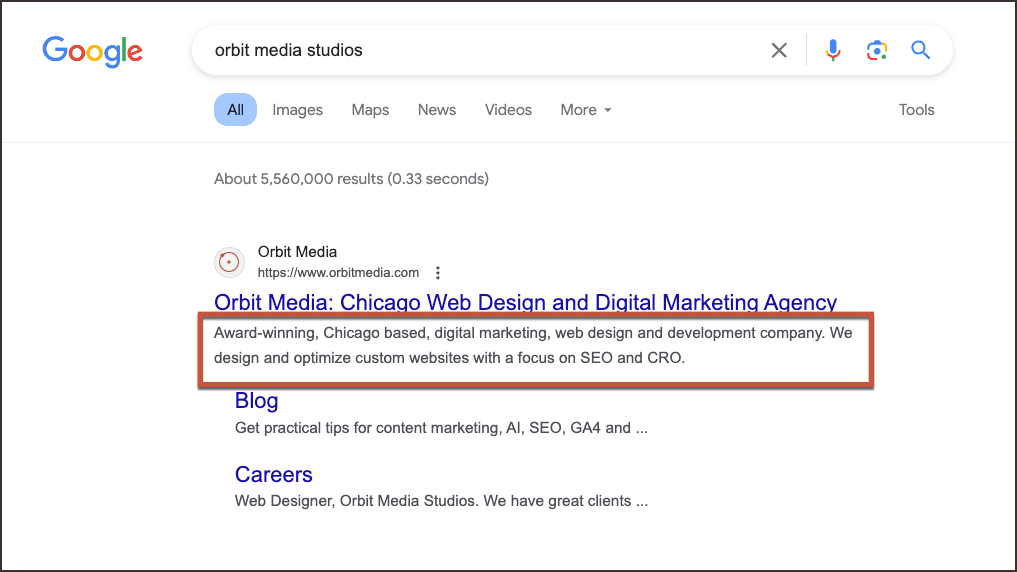
Example of a meta description in a search engine result:
4. Targeted and unique content
Your content is the core of your SEO efforts. High-quality content directly addresses the needs and search intent of your target audience. Before writing, ask yourself: What problem is the user trying to solve? What question do they need answered?
Your goal is to create the most comprehensive and helpful resource on that topic. This means going beyond just including keywords and focusing on providing real value, which keeps users engaged and signals to search engines that your page is a relevant result.
Content should be relevant and unique
With many recent and continuous updates to Google’s core algorithm, it is extremely important that your content is unique and relevant. If you have multiple pages with the same content (or if you have your content on other people’s websites), you run the risk of competing against yourself and negatively impacting your search rankings.
Keyword frequency
Using the keyword research you’ve conducted, include semantic keyphrases and target keywords throughout your content. SEO best practices are to use these important keywords in your headings, especially your H1, the first paragraph and a few more times throughout the page. Though you should avoid something called keyword stuffing– which refers to unnaturally forcing keywords into web pages with the hopes of ranking higher.
So, don’t go overboard, but you should aim to include your targeted keywords about 3-4 times within your content (depending on the length), as well as semantic keyphrases.
Looking for more tips on auditing and improving content? Check out our guide to AI-powered webpage optimization.
Best practices:
- Create quality content that is extremely relevant to the target keyphrase.
- Depending on the topic and length of content, you should aim to use your keyword phrase 1-4 times within your content (but don’t abuse it).
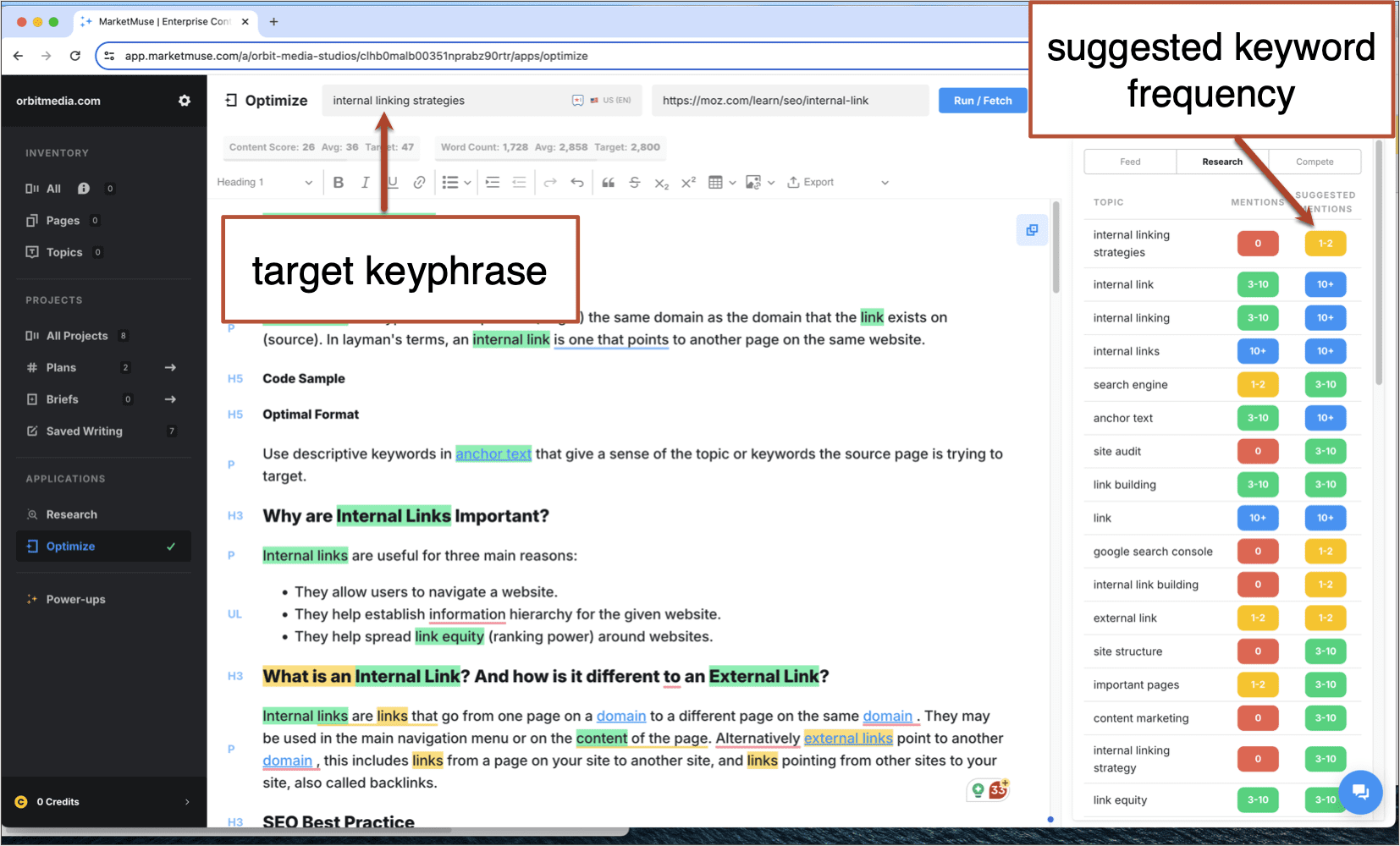
- Include links from other pages within your website that point back to this page (read more about internal linking strategies).
- Create unique content. Before creating a new page or blog post, ensure that you aren’t already ranking for the targeted keyphrase elsewhere.
- Avoid directly duplicating content for press releases, blogs, a guest blog post, etc.
Here’s a screenshot from MarketMuse showing the suggested frequency for a target keyphrase and various semantic keyphrases:
5. Relevant URL
The words in a page URL are a quick way to tell users and search engines what the page is about. If a URL is confusing, long, or unrelated to the page content, it may make it less desirable and more difficult for users to share and land on the page. On the other hand, a short and straightforward URL will be more desirable to readers and search engines.
URLs are considered to be a minor ranking factor for search engines, but they can still be optimized to better suit your users. Inserting your target keyword into the URL may play a role in search visibility, so do include it when it makes sense.
Best practices:
- Include your target keyword.
- Avoid using full sentences and mixed cases.
- Replace underscores(_) with hyphens (-).
- Avoid using spaces, characters and excessive or unrelated numbers.
6. Headings
Headings are extremely important for many reasons. Not only do headings support accessibility on a webpage, they make content easy for users to read and they help Google understand the structure of your page.
Think of headings as an outline of your content. The header tag, also known as the H1 tag, is much like the subject line of your web page. H2s can cover a different section or subtopic, and if needed, H3s and H4s can cover sub-subtopics.
You should only use your keyword phrase once in the H1 tag. You may also use other keywords and keyword variations in subsequent headings to provide context to Google and users about the structure and context of your content.
Best practices:
- Use your target keyword phrase once in your H1 tag.
- Use the H1 as the page title or subject line.
- Use other heading tags as needed, following a hierarchical structure.
Example of an H1 tag being optimized for ‘web design’:
7. Internal page linking with anchor text
Internal linking refers to a hyperlink on a page that points to a different page on the same website. Internal linking is important for SEO because:
- It helps strengthen keywords and signals that the page is valuable to search engines
- It allows users (and search engine robots) to easily navigate through the website, discovering new pages and better understanding your site structure
- It tells the search engines that the page is relevant for that keyword phrase.
Best practices:
- Use descriptive anchor text: When adding an internal link, use specific keywords in the anchor text (the clickable text). For example, link the phrase “our web design services” to your services page, rather than using generic text like “click here.”
- Link to relevant content: Ensure the links point to pages that provide additional context and value to the reader, helping them navigate your site logically.
- Avoid linking errors: Regularly check for and fix broken links (links that lead to a 404 error page), as these create a poor user experience and can negatively impact your SEO. You can run checks using a tool like Screaming Frog.
- Ensure your link structure is logical and not overly complex.
Example of how to use anchor text in your internal links:
“SEO agency” links to Orbit’s SEO service page.
8. Image alt text and filenames
To ensure your images are following best SEO practices, it’s important to know how to optimize your alt tags and filenames.
Alternative text, also known as alt text, alt description and alt tags, is text that describes what an image is depicting. All images should use appropriate alt text, as it can be helpful for SEO and improves the accessibility of your page.
Search engines use alt text to gain more context about the image, helping crawlers properly index and rank the image. Alt text also provides readers using some assistive technologies, such as a screen reader, more information about what images are on the page.
Proper file names can also improve SEO. When possible, try and include your keyword phrase in the name of the image, but don’t force it. This can help your image and your page appear in image search results.
Best practices:
- Include alt text for all images on your website, ensuring the text is descriptive and accurate.
- Include your keyphrase in the image filename when possible.
- Use dashes between the words, rather than underscores ( purple-hat.jpg rather than purple_hat.jpg).
- Do not use non-alpha characters in your image or file names (so no %, &, $, etc…).
9. Readable content
Focusing on readability is not a huge factor in search engine rankings, but it can improve the user experience. Factors such as bolding text, using bullet points and keeping your paragraphs short can help users more easily scan the content, finding the keywords they are looking for. It’s also important that your audience can understand your content, meaning you should avoid using industry jargon and stick to simple, clear language.
When your content is informative and easy to read, users are more likely to stay on your page longer. This means a lower bounce rate, which signals to search engines that your site is relevant, helpful and should be high ranking.
So, do add subheadings, bulleted lists, visuals and bolded text, but don’t overdo it. Excessive formatting of the page can be off-putting.
Best practices:
- Keep your paragraphs to about three sentences long. Extremely long sentences will lose the users’ attention.
- Use bullet points, subheadings and bolding to break up large blocks of content. Users tend to scan content looking for keywords.
- Do not overuse bullets and bolding.
Example of easy-to-read content:
10. Schema markup
Schema markup, also known as structured data, allows search engines to better understand the content on your page. Adding schema markup to a page means using code that signals what the information on that page is about. Some common types of schema include:
- Events
- Products
- Reviews
- Local places
- Health and medical
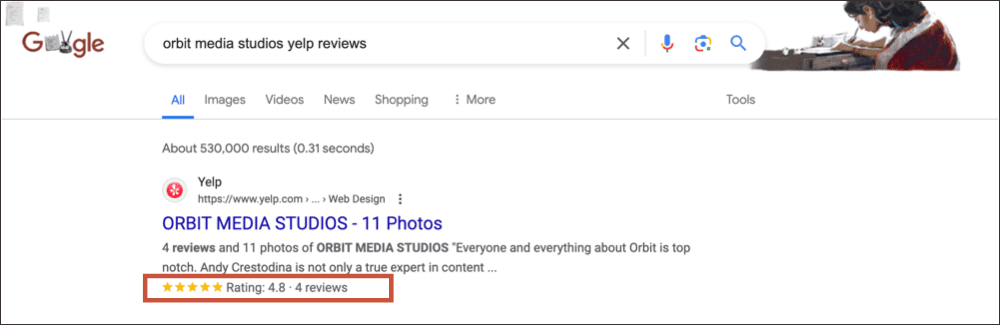
Using schema can lead to a rich snippet win in the SERP. This means even more details about your page are shown on the result page, taking up more valuable space, drawing attention to your page and increasing clicks. Schema can also be extremely helpful for local SEO. (Learn more in this checklist of local SEO ranking factors)
Best practices:
- Use the correct schema type. Research your options and find the type that most accurately matches your content.
- Try to provide as much detailed information as you can. The more properties you fill out, the more information the SERP can provide.
- Avoid using schema that isn’t relevant to your page or content.
Here’s an example of review markup being displayed in search results:
11. Monitor your performance with key tools
SEO isn’t one and done. To truly see growth and build a solid foundation, it’s important to regularly monitor your performance and optimize important content.
To get insight into your performance, you’ll need access to SEO tools. There are two essential free tools from Google that can get you started:
- Google Search Console: This tool helps you understand how Google sees your site and how users are finding you through search results. You can use it to track which keywords you’re ranking for, submit sitemaps, and identify technical issues or crawling errors that might be hurting your performance.
- Google Analytics: This provides detailed data about the traffic to your website. You can see how many people are visiting, where they’re coming from (including organic search), which pages are most popular, and how users are behaving on your site. Regularly checking these tools will allow you to make data-driven decisions to continually refine your SEO strategy.
An overview of technical SEO best practices
In addition to off-page and on-page SEO, technical SEO plays an important role in the user experience of your website, crawlability, and more. Here are some things to consider:
Optimize for page speed and core web vitals
A fast-loading website is essential for a good user experience and is a confirmed ranking factor. Google measures this through a set of metrics called Core Web Vitals, which assess a page’s loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures how long it takes for the largest content element (e.g., an image or block of text) on the page to load.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Measures how quickly your page responds to user interactions, like clicks or taps.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability, looking for unexpected shifts of page content as it loads.
You can use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to analyze your site and get specific recommendations for improving your Core Web Vitals.
Ensure your site is mobile friendly
With the majority of web traffic now coming from mobile devices, having a mobile-friendly website is non-negotiable. Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it predominantly uses the mobile version of your content for indexing and ranking.
Your site should be easy to navigate on a smaller screen, with readable text, tappable buttons, and fast loading times to provide a seamless user experience for mobile visitors.
Technical SEO best practices:
- Compress and resize images to keep file sizes as small as possible
- Enable browser caching
- Prioritize responsive website design
- Limit the use of scripts from external systems, including plugins, pop-ups, and other webpage elements
- Clean up and limit redirects
An off-page SEO overview
Off-page or off-site SEO is all about building credibility and signaling to search engines that your site is a reputable source of valuable information. The most important off-page factor is building high-quality backlinks.
A backlink is a link from another website to yours. Search engines view backlinks as votes of confidence; the more reputable websites that link to you, the more authority and trustworthiness your site gains. You can earn backlinks by creating valuable, shareable content, guest blogging on other sites in your industry, and building relationships with journalists and influencers.
Learn more about user signals and SEO here
Off-site SEO best practices:
- Look for authoritative websites in your niche. Reach out to the marketers that run those websites about guest-blogging and link building opportunities.
- Conduct and publish research and useful data. Surveys, industry reports, and data-driven content can help you earn more backlinks.
- Write press releases. If you have a business change, new service or product offering, or other piece of related business news, you may be able to score links from media outlets.
- Encourage reviews and testimonials from happy clients. Reputation management is another key part of off-site SEO and trust building.
That’s all, folks!
I hope this on-page SEO checklist will prove helpful for your web optimization efforts.
There are two things to keep in mind with SEO: one size does not fit all, and SEO is ever-evolving. Your SEO strategy should be customized to meet the needs of your business, and will always be a work in progress.
If you’re looking for quality SEO services from an experienced agency, Orbit can help. Let’s get started →