It’s that little search box in the header of your website. Visitors use it to search for things. It’s often called “Site Search,” and it helps people find what they’re looking for fast. It’s a way to help your visitors.
But for you, the marketer, it’s a listening tool.
The site search tool gives you a peek into what your visitors want from you and your website. And sometimes, it shows you what your visitors can’t find.
It’s an amazing way to find and fix content gaps. In this post, we’ll do four things:
- Setup/Reporting: How to see your site search terms reports in GA4
- Listen: How to analyze these reports
- Empathize: Check to see if visitors are finding what they’re looking for
- Take Action: Create (or optimize) content based on your new insights into your visitors’ needs
We’ll do it all using a custom dimension and a “free form” exploration. We’ll walk through the steps for setting this up in GA4.
A lot of websites don’t even have a search tool (only 54% do according to our research). Some sites have them in just one section (on this website, it’s just on the blog), and some sites have more than one search tool!
Here’s how to do site search analysis in GA4.
Site Search setup in Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
Just as Google Search Console shows search activity on Google, this GA4 Exploration shows search activity on your site. As long as the GA4 tag is installed in your Google Tag Manager container, you’re ready to get started.
There’s an extra bit of setup we need to do first because the dimension we’re looking for needs to be registered as a custom dimension before it’s available to use in an exploration. That sounded technical, but it’s not complicated. Here’s how to set up search_terms as a custom definition, then build a exploration that shows what are visitors are searching for.
- From the Admin section, go to Data display > Custom definitions.
- Click on the blue “Create custom dimension” button
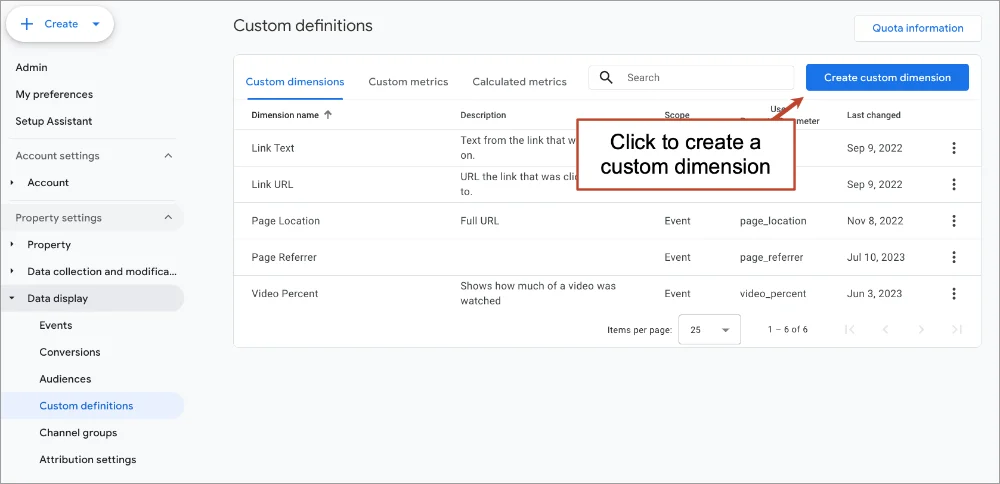
- Enter “Site Search Terms” as the dimension name
- Select “search_term” as the parameter
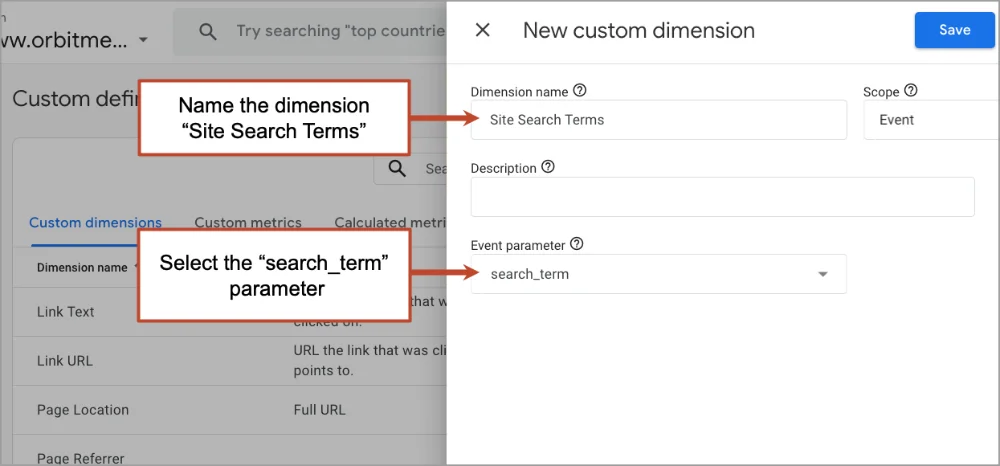
- Click Save
Now we’re ready to create the exploration.
- Go to explorations and click on “Blank”
- In the top right, give your exploration a name, such as “Site Search Analysis”
- In the Variables column, click the plus sign next to DIMENSIONS.
A list will slide in from the right. Use the search tool at the top to find “Search Site Terms” and select it. Next search for “Event name” and select it. Click Import. - In the Variables column, click the plus sign next to METRICS. Again, a list will slide in from the right. Use the search tool to find “Event count.” Select it and import it.
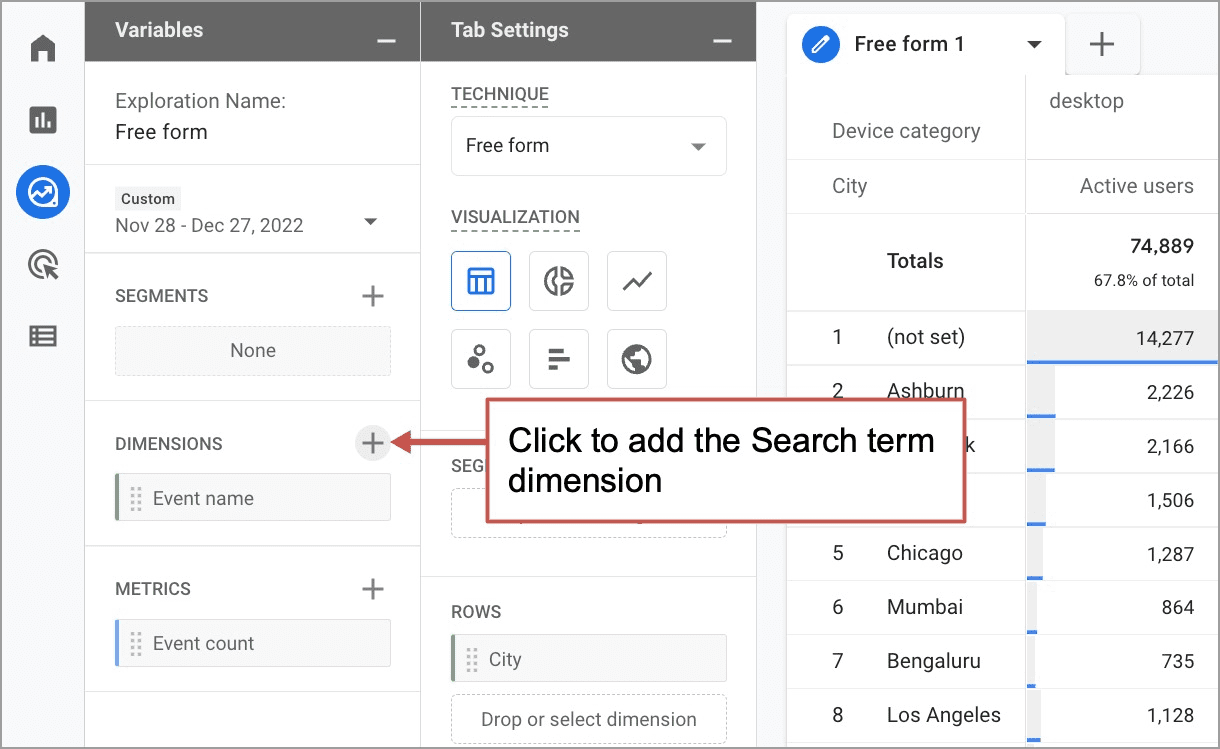
- Drag the “Site Search Term” dimension from the Variables column into the Rows box in the Tab Settings column. Drag the “Event count” metric into the Values box.
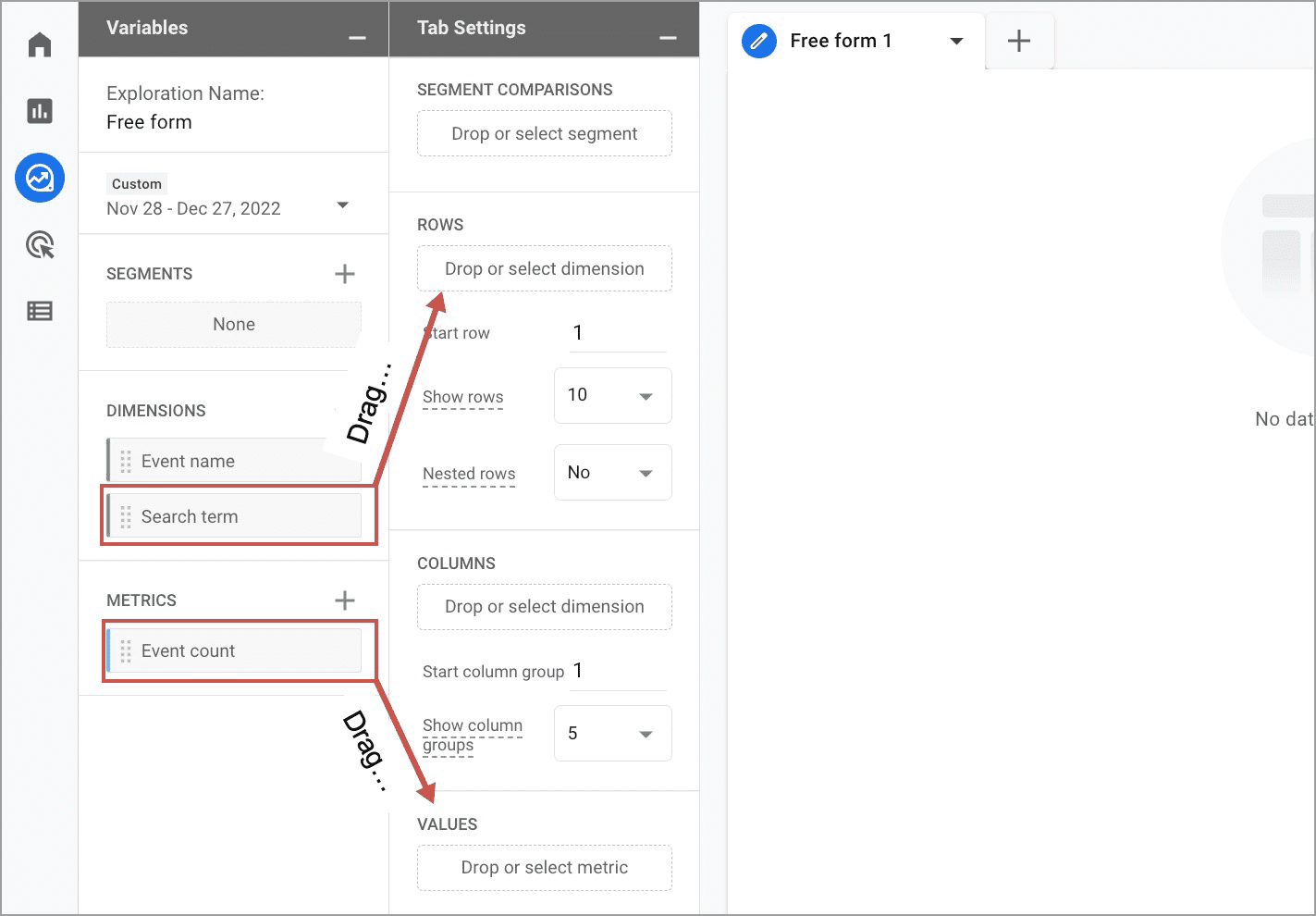
- You’ll now see the exploration on the right, but notice how the first row is blank but shows a very high event count. This is the number of times visitors didn’t search. It’s not useful. If you’d like to remove that, you can do so with a filter. Drag the “Event name” dimension into the Filters box. Set the filter to “exactly matches” the event view_search_results.
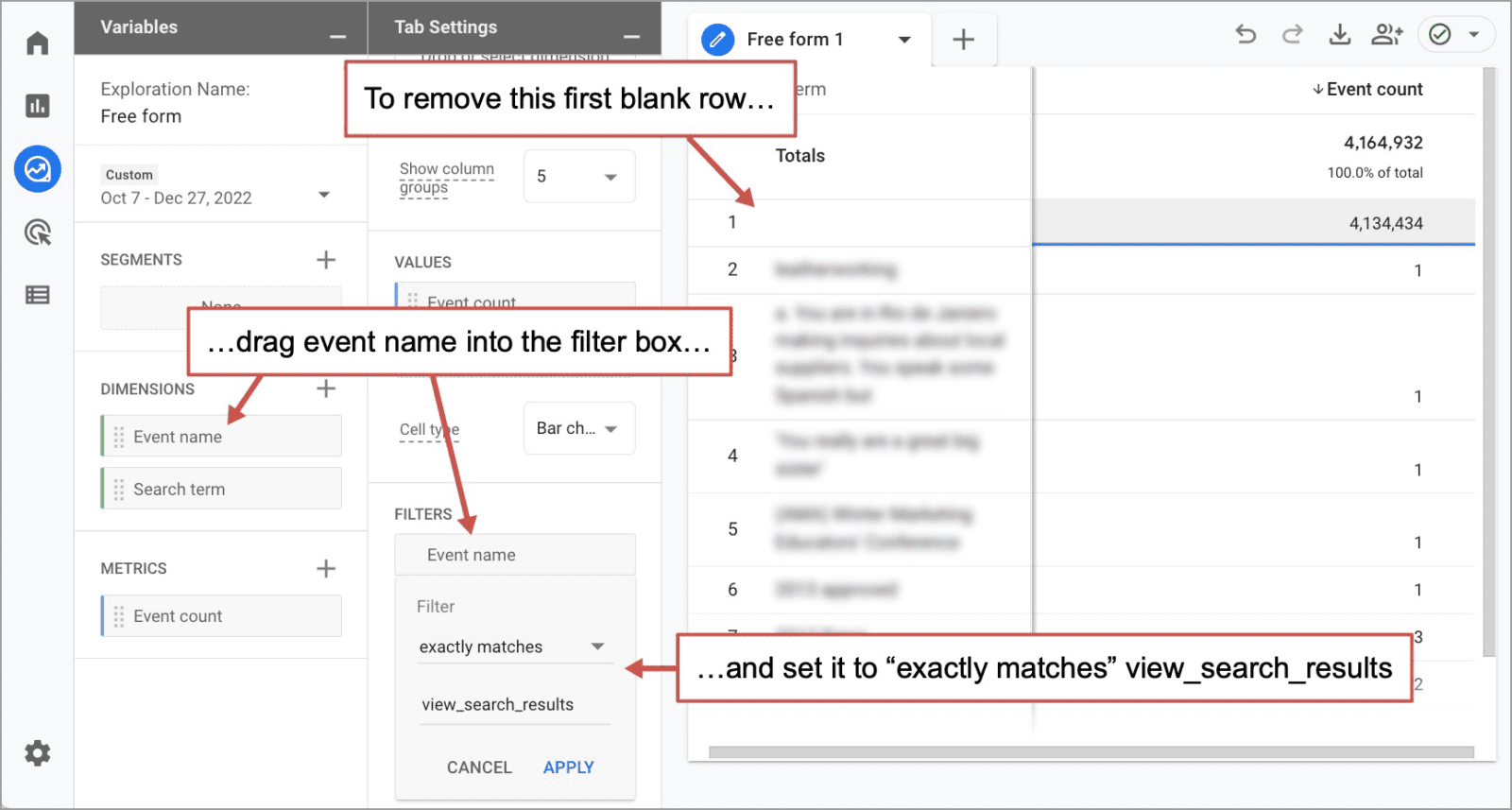
All done! Now we can eavesdrop on our visitors a bit, see what they’re looking for.
How to analyze your Site Search reports in Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
The exploration we created shows the list of the phrases that people search for using your site search tool. It will look like this:
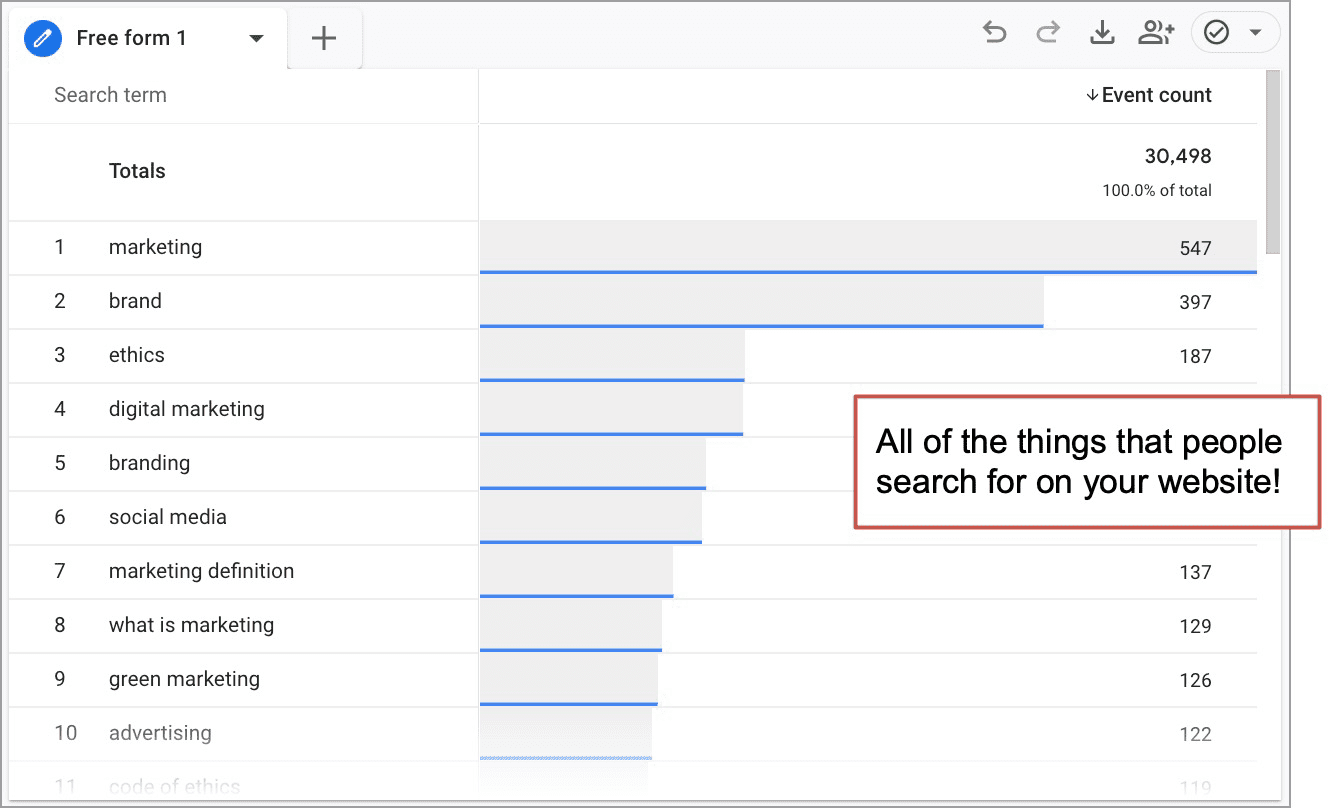
Are visitors finding what they’re looking for?
The insights from this search terms report are often so obvious that I’m guessing some of you readers just left and will never finish this article. The usability problems and content gaps are leaping out of Analytics and onto your to-do list for today.
But if you’re still here, let’s do some analysis.
First, pretend you are the visitor and go to your website and search for the top phrases that your visitors are searching for. Look at the search results. What do you see? Anything unexpected? Are you having the same experience you want your visitors to have?
I bet I just lost some more of you. The issues are so obvious that you don’t need any suggestions.
Here are four examples of analysis and actions based on site search data from your Analytics. Each starts with the user’s experience and ends with an action you can take to improve your website.
 |
William Tseng, Lucidworks“Visitors who use your search tool are some of your most engaged visitors. They want something so bad they’re willing to drop the mouse and start typing. Make sure your tool is tuned up, and keep an eye on those search terms. They’re often a gold mine of opportunity for website improvements.” |
Example 1: “I don’t understand your navigation labels”
You are a patio furniture company. You sell all kinds of outdoor stuff for decks, patios and pools. Your navigation might look like this:
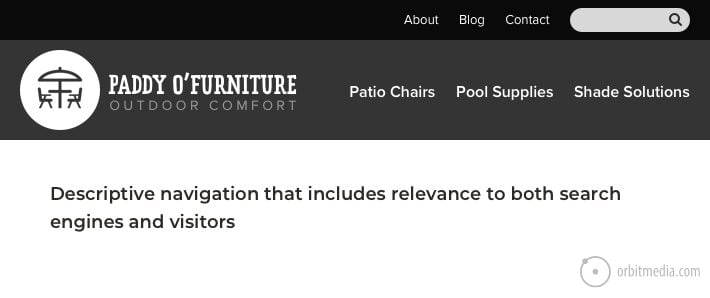
And here is the GA4 exploration showing the search terms and their relative popularity:
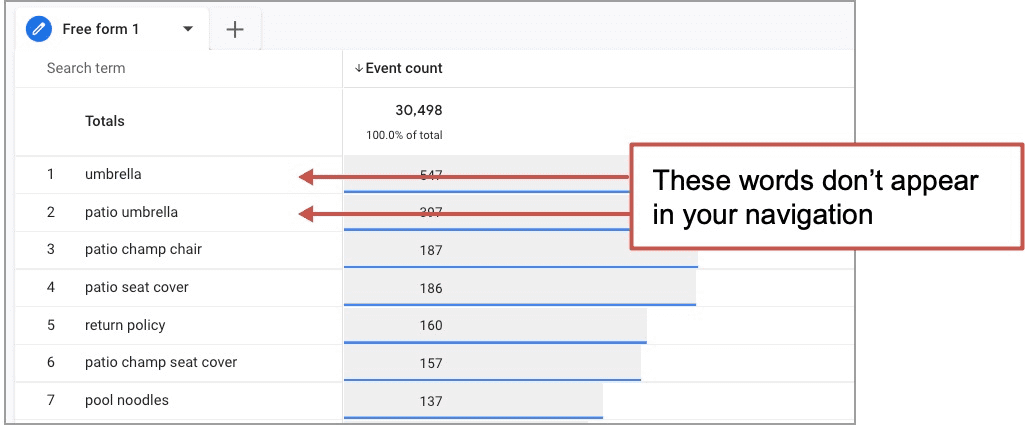
See the problem? Your visitors are searching for “umbrellas” because they don’t see it in your navigation. Your navigation says “Shade Solutions” which is a weird term that people never say. Unless you’re a marketer… “It’s going to be hot at the beach today. Don’t forget your shade solution!”
Action! Change your navigation labels to align with the phrases your audience is searching for.
Example 2: “I want to find something faster”
You are a construction equipment dealer. Your website has a resource center with guides for buying all kinds of machines. It’s a big section, so it has a search tool.
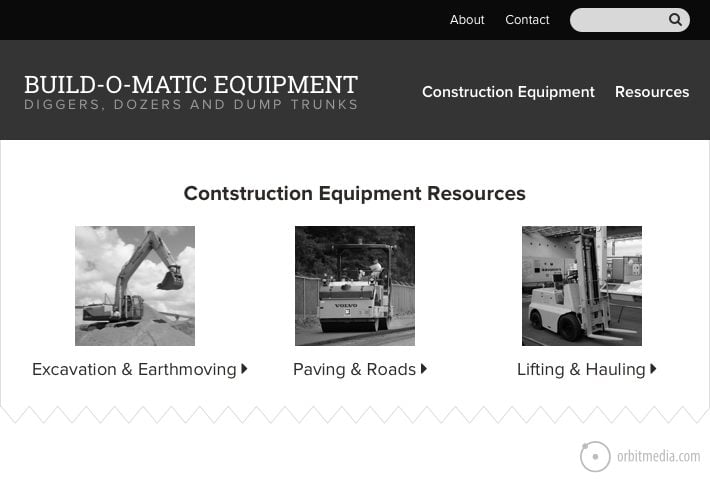
And here is what your exploration showing search terms look like.
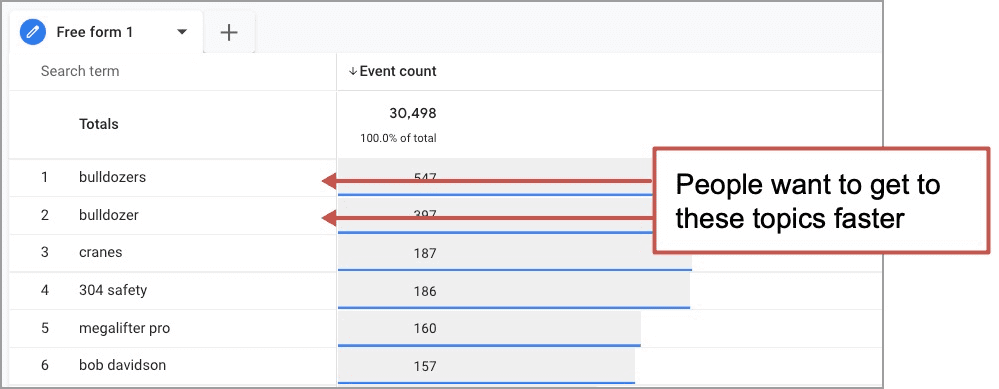
See the opportunity? The page gives them three big options. But since they don’t see what they want, they search.
Action! Add “bulldozers” to one of the labels, give it it’s own section or make one of the images a bulldozer!
Example 3: “I can’t find what I want”
You have a toy store. Your site has lots of pages and products, so of course, there is a search tool. When you take a look at your search terms, you can see that visitors are looking for some very specific information: “unicorns”
But what if the visitor searched and left the search results page without clicking on anything? They must not have found what they were looking for. They left without finding anything.
So what are your visitors searching for but not finding? This question is answerable in your Google Analytics account. We just need to see which pages with searches (page path + query string) were also exit pages.
So we need to add the Exits metric to our exploration.
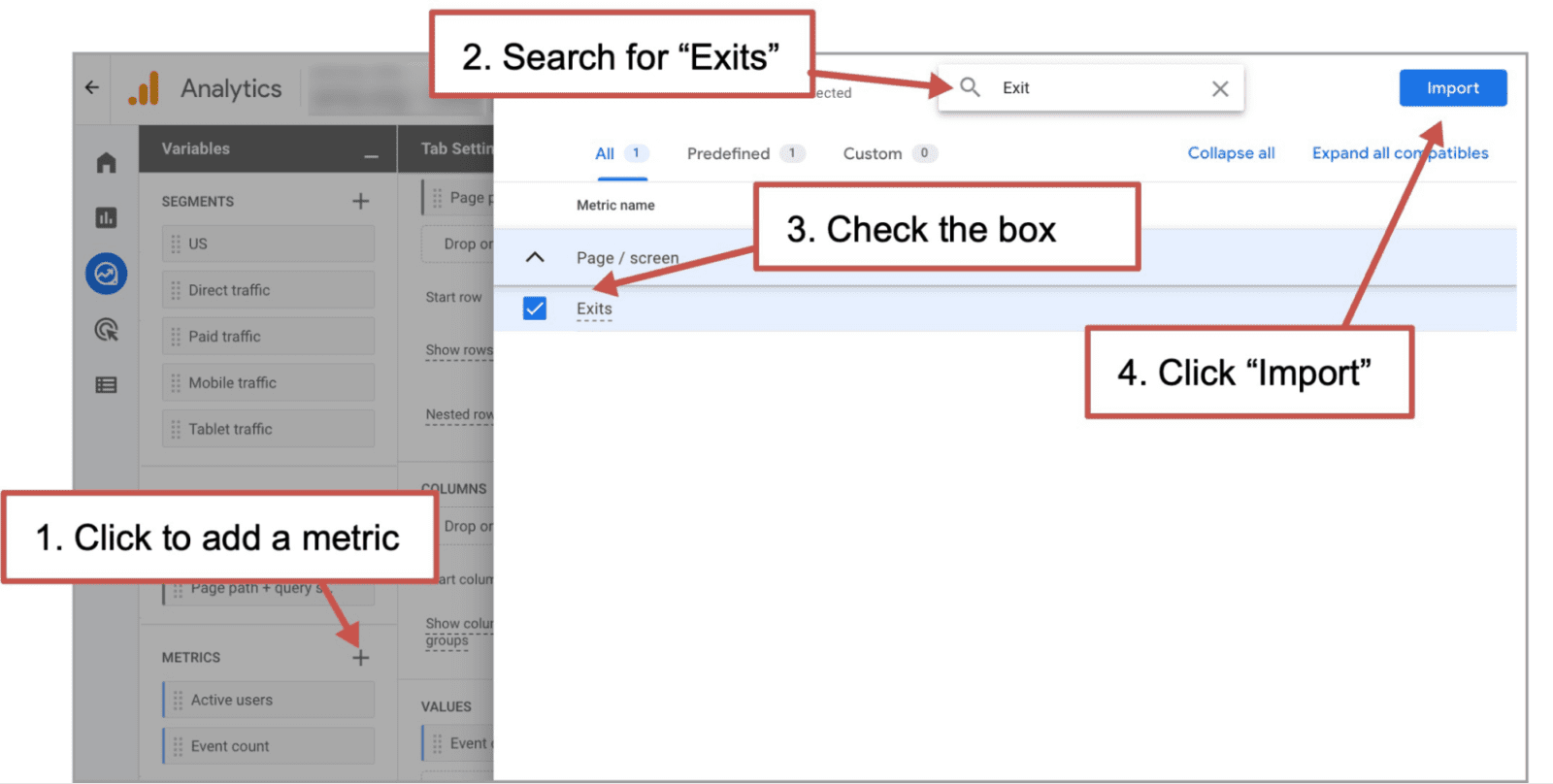
- In the variables column on the left, click the plus next to Metrics
- A list of metrics will slide in from the right. Search for “Exits”
- Check the box next to Exits
- Click the blue “Import” button in the top right corner
- Now drag the Exits metric into the “Values” box in Tab Settings
- Sort by Exits (descending)
Here’s what you’ll see:
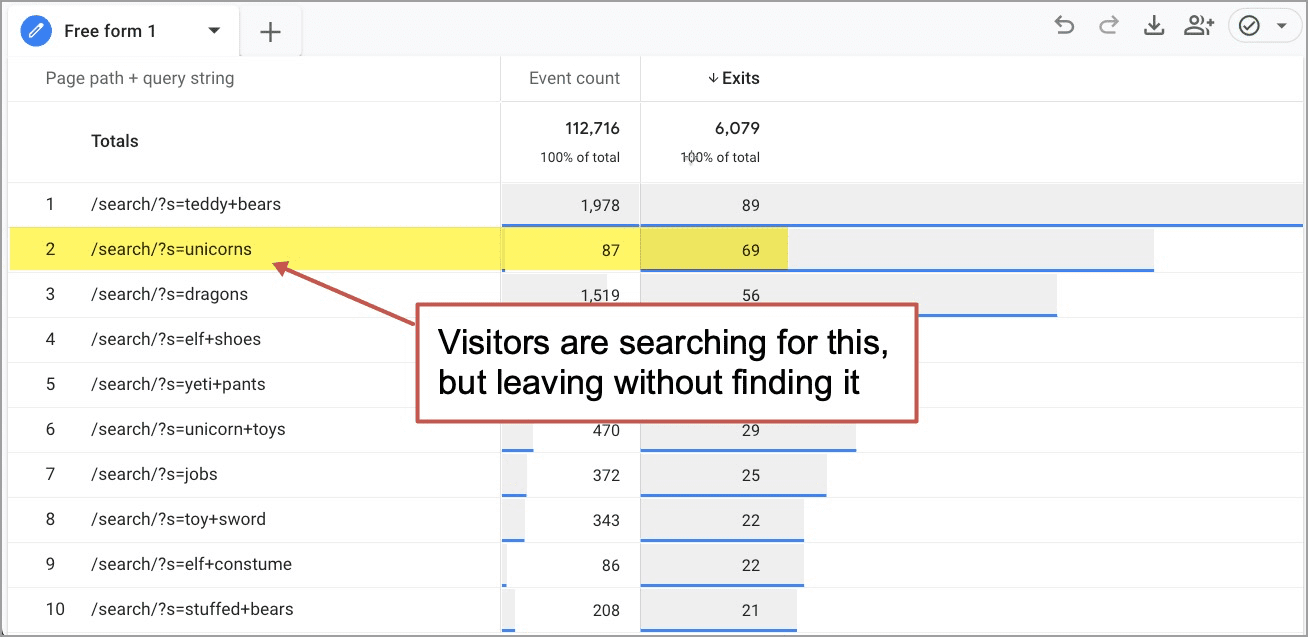
Now you’re looking at a list of what people search for and the last page they visited. You can tell right away that some people are looking for unicorns but not finding any.
They never clicked. They left without the information they needed. That’s why we call this The Report of Broken Dreams. It shows you what your visitors searched for but did not find.
Action! This should be an easy fix now that you have search exit data.
- Search for the phrase yourself. What do the search results show?
- If you don’t already have a page on this topic, make one!
- If you do have a page but it’s not ranking, update the page so it ranks higher for that keyword in your site search results. Put the phrase in the title, header and body text.
- Now search again. All better?
Site search SEO is a type of optimization that everyone should love. Make your own content rank in your own search tool on your own website.
Example 4: “This page isn’t satisfying”
You are a tax advisor. Your firm offers a lot of services, your site has a lot of pages, so of course, you have a search tool.
In a brilliant act of data-driven empathy, you use Google Analytics to find out where and when people use your search tool. You do this by creating a Path Exploration. Unlike the usual user flow analysis, we’ll start the ending point, which is the search results page:
- Click to create a path exploration
- Click “Start over” in the top right
- Drag the Page path and screen type node type into the Ending Point box
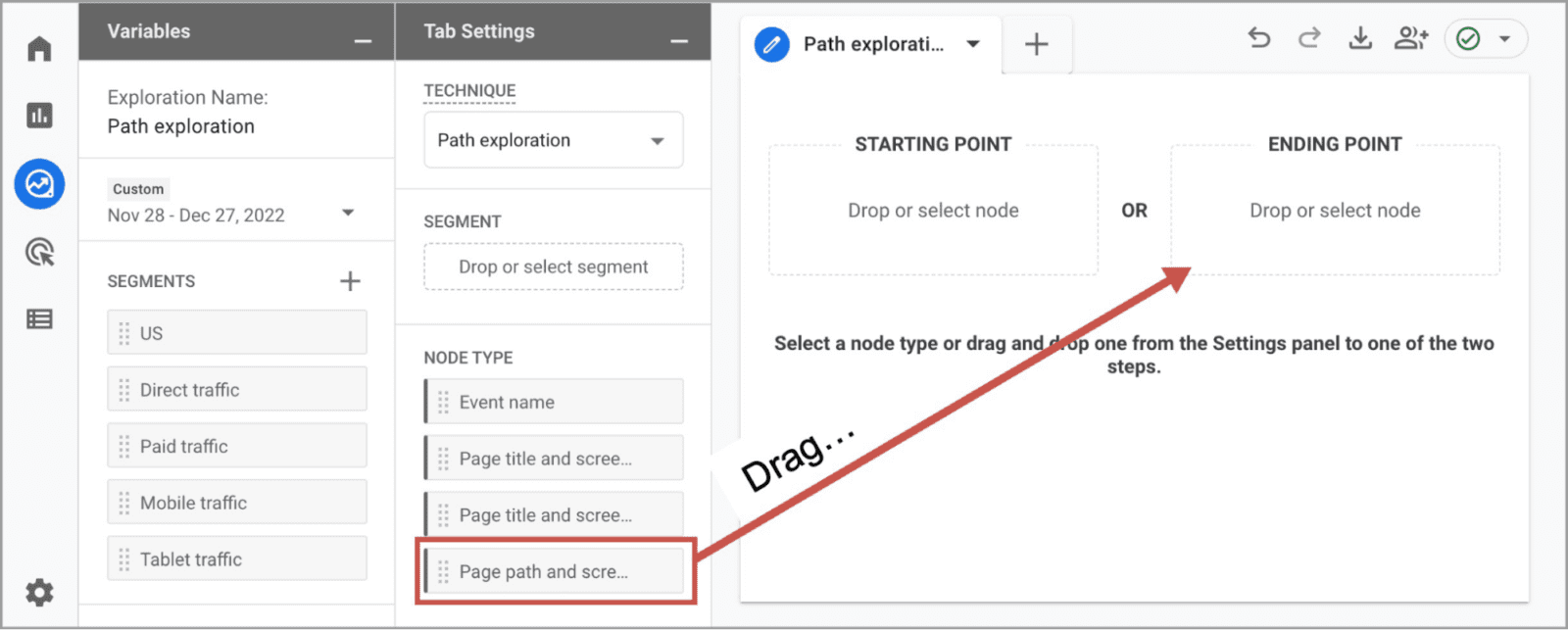
- A list of pages will slide out from the right. Probably, the URL of your search results page isn’t high on the list, so search for it and select it.
Now you’re looking at a list of the pages from which visitors use your site search tool. Not surprising, a lot of visitors search right from the home page. But what about the other pages? Are they missing some key information? It’s very likely that these pages are not satisfying your visitors information needs.
This is a list of pages with content gaps.
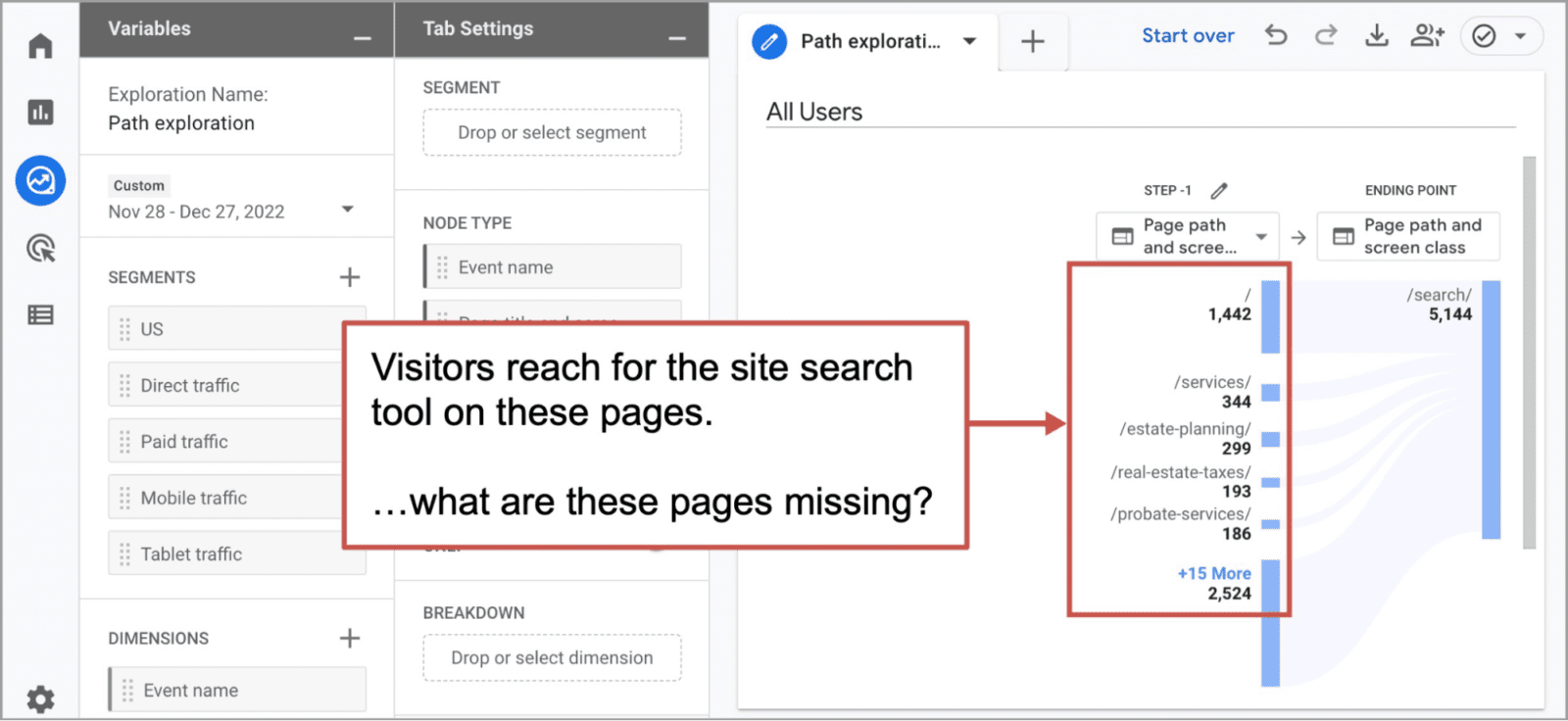
If you reference this list against your list of top search terms, you may quickly realize which pages are missing which information.
Action! Add the missing information to the page. If this info is already on another page, you can also just add a prominent link, directing the visitor to the second page.
Data-driven empathy vs. unmet information needs
Your visitors would rather click or tap than type. They don’t really want to use your internal search tool, but if they don’t see what they want, they’ll use it as a last resort.
It’s a far, far distance from the mouse to the keyboard. It’s even further on mobile. Don’t force them to make the jump. Check your Google Analytics site search reports to see who is crossing that chasm and then build a bridge so your next visitor doesn’t have to.
Bonus! Is Google stealing your site searchers?
When you search for your brand in Google, you probably see your homepage ranking high with four or six links to interior pages underneath in two neat little columns. Those are your “sitelinks.”
But do you see anything else? Do you see a search box right above your sitelinks? This is common for big sites and well-known brands.
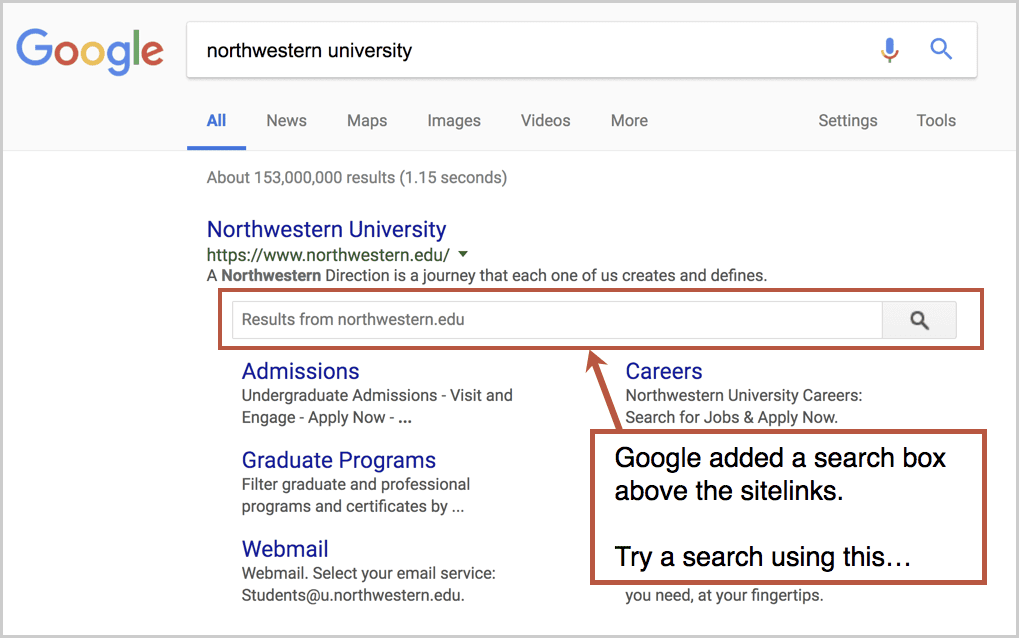
If you do, try a search using that search box. What do you see? Are you on a search results page within Google?
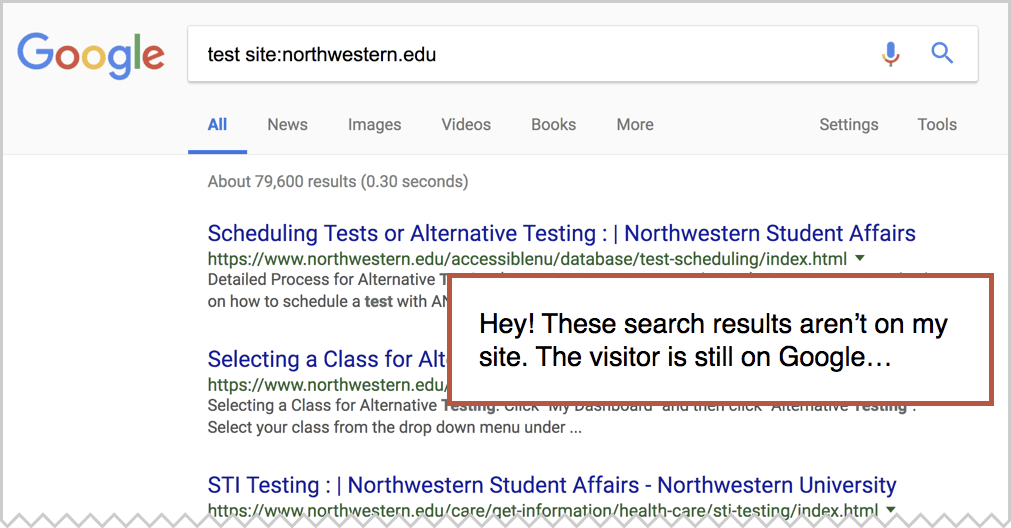
If so, Google keeping your potential visitors a little longer than they should. They’re not sending people to your site to see your search results. They’re taking away your ability to listen. You have two options:
Option one: Send those visitors to your site for their search results.
This will let people search your content faster, right from Google, but it gives you the visitor. To do this, add this code to your homepage, editing the URL and target fields for your site.
<script type=”application/ld+json”>
{
“@context”: “http://schema.org”,
“@type”: “WebSite”,
“url”: “https://www.example-petstore.com/”,
“potentialAction”: {
“@type”: “SearchAction”,
“target”: “https://query.example-petstore.com/search?q={search_term_string}”,
“query-input”: “required name=search_term_string”
}
}
</script>
Option two: Remove the Sitelinks Search Box from Google
If you want people to visit you first and search your content later, you can remove the search box from above your sitelinks, just like Amazon does, by adding this code to your homepage.
<meta name=”google” content=”nositelinkssearchbox” />
Now your visitors will have to come to your site, experience your brand and your design, before searching your content.
Got any data-driven empathy tips of your own? Share with your fellow readers by leaving a comment below!