Do social media interactions affect search engine rankings? The short answer: Yes. But not how you think.
Social media activity affects rankings in several ways. But the direct benefit is very limited and the indirect benefit is widely misunderstood. In this post, we’ll deconstruct both.
First, Let’s Look at the Evidence.
The 2013 Moz Search Ranking Factors study shows that pages with Google+1, Facebook likes, tweets, and comments tend to rank higher.
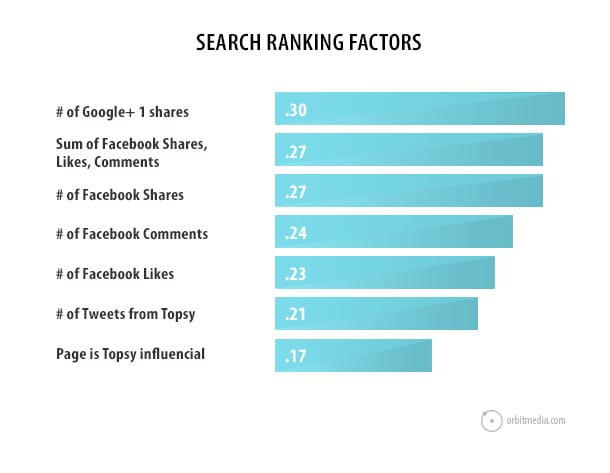
The study shows a connection between social activity and higher rank. Pages with Google +1s, Facebook likes, and tweets tend to rank higher. But this is a correlation, not causation. It’s critical to understand that difference.
Lots of things are correlated, but that does not imply that one causes the other. Consider these interesting correlations…
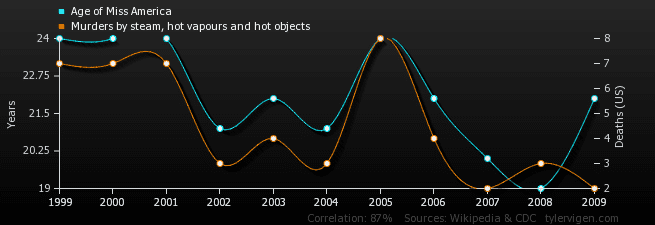
Age of Miss America correlates with murders by steam and hot vapors (correlation of .87)
Number of movies Nicolas Cage appeared in correlates with drowning in swimming pools (correlation of .66)
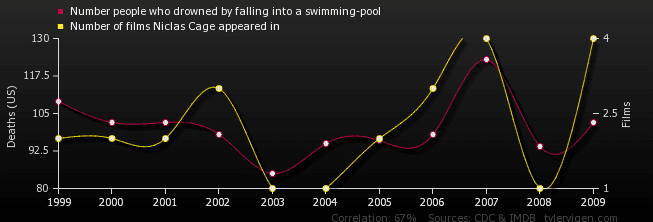
(source: Tyler Vigen’s Spurious Correlations)
Are Nicolas Cage movies causing people to drown in pools? Can we reduce the murder-by-steam rate by crowning younger women as Miss America? Not likely. Correlations are just connections. We have to look closer to find causes.
Where There’s Smoke, There’s Fire. Right?
Smoke doesn’t cause a fire. But catch a whiff and you’ll start looking around. Why does social activity correlate with search? Does sharing affect rankings? Does a Facebook or Twitter following affect rankings?
Directly? No. Here’s a quote from Google…
…you have this many followers on twitter or this many likes on Facebook, to the best of my knowledge, we don’t currently have any signals like that in our web search ranking algorithms. – Matt Cutts, Google Webmasters YouTube Channel, 1/2014
That’s a no. But there are three actual connections between social and search. The first two are indirect correlations and the third is actual causation.
1. Sharing Can Lead to Links …and Higher Rankings
Social sharing directly increases the visibility of a page. That increased visibility means it may get noticed by a creator of content, such as a blogger, journalist, or author. That creator may mention it in a subsequent piece of content. If they linked to it, that page is then more likely to rank.
For sharing to affect rankings, a lot of things have to go right…

The social activity (sharing) affects rank only if it increases visibility among content creators AND those people found it so useful they linked to it.
“It’s not the actual social activity that matters, but what happens as a result of that activity. Optimizing and maximizing creator impressions increases the chance of obtaining links from the group of people who power the link graph.” – AJ Kohn, Blind Five Year Old.
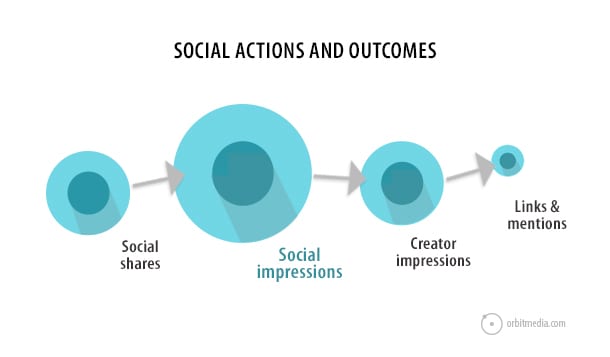
One way to help this process along is to actively build relationships with content creators, sharing content with them specifically. This should sound familiar to anyone who understands PR.
Social influencers amplify impressions, but content creators create the ranking benefit. They include:
-
Bloggers and blog editors
-
Journalists
-
Podcasters
-
Academic Researchers
-
Event producers
If rankings are important to you, relationships with creators of content are important to you. Content creators are a hidden, but important, target audience for most businesses. But many of them don’t realize it.
2. The Correlation Between Social Media and “User Interaction Signals”
Imagine this: a visitor searches for a phrase. They now see a search results page with 10 blue links. They click one and land at a page that doesn’t seem to help them. They hit the back button. That’s a bounce (a one-page visit).
Then they click another link on the search results page and find a more helpful page. They stay for a few minutes. Maybe they click around…
Google was watching. Remember, they own the search engine, but they also probably own the browser (Chrome is the world’s most popular browser: source) and Analytics on both sites (most websites use Google Analytics: source) They know that the searcher stayed on one page much longer than the other.
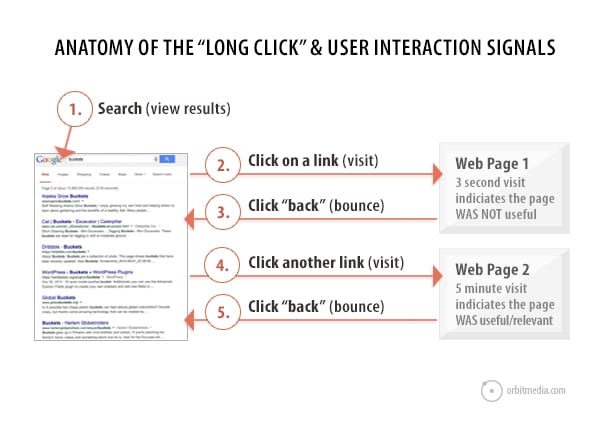
Search engine researchers call this the “long click.” It should be obvious that Google would use this as an indication of quality and relevance.
The specific stats in play here are “time on site” and “bounce rate.” They are both considered “user interaction signals” and show that the visitor was engaged. What else correlates with engagement? Social interactions.
Likes, shares, +1s, tweets, and comments are indications that people thought the page was good. And pages that people like tend to rank higher. Social media interactions correlate with quality and quality correlates with higher rankings.
For the record, there are other ways (beyond social media) to improve the user interaction signals on a page. Naturally, they all relate to quality.
-
Formatting: don’t hit visitors with a wall of text. Break up paragraphs, use bullet lists, bolding, internal linking, subheaders, etc.
-
Media: add multiple images, video, audio, or anything else that a visitor is likely to engage with.
-
Length: longer pages tend to rank higher for a good reason. They are more likely to be authoritative.
-
Stimulate comments: ask a question, invite dissent, spark a conversation. Comments are a type of social activity that directly affect user interaction signals.
The bottom line: If you want to rank higher, make a page that people love. Sound familiar? It should. This has been what Google has been telling us all along. Of course, you need to pay attention to keyword research and keyword usage, but focus on the visitor, the experience of humans.
A page that people are likely to share is a page that is more likely to rank.
What’s good for social is good for search.
 |
“In the world of paid traffic in which we specialize, we often discuss search versus social in terms of demand generation. Search is great at fulfilling demand, while social is unique in the digital realm for its ability to create demand.
Depending on where a customer (or lead, or blog reader) is on their journey, search and social can and should reinforce each other, and very often both play prominent roles at different points in the same path to purchase.“ Chris Madden, Matchnode |
3. How Google+ Activity Directly Affects Rankings
There are two ways in which rankings are directly affected by Google+ activity. They both rely on the searcher being logged into their Google+ account.
-
Google+ posts rank in Google
Actual Google+ posts rank almost instantly for phrases included in the post, for anyone who has added you to a circle. This is why smart G+ users write posts with “titles” which are usually bolded headlines at the top of the post. Text is bolded in Google by putting asterisks before and after the text. -
+1’d content ranks higher in personalized search results
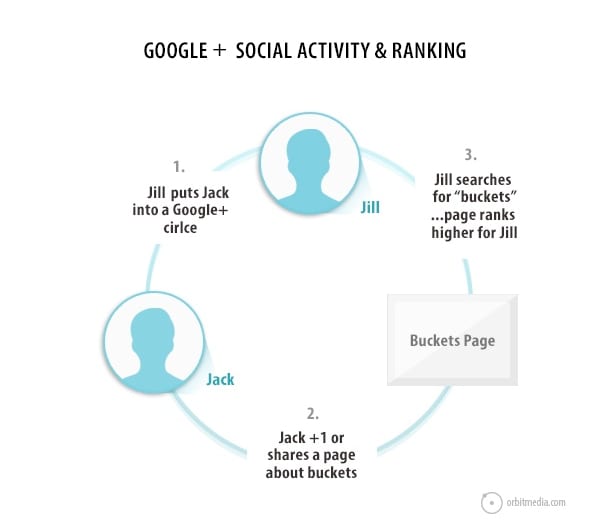
Google search results are personalized for people who are logged in to Google+, provided they have connected with people who have interacted with content. Rankings are directly affected. Here’s how it works:If Jill puts Jack in a circle, and Jack +1’s a page about buckets. That page will rank higher when Jill searches for “buckets.” She will also see that Jack likes this page, right there in the search results.
Here’s what it would look like in the search results page.
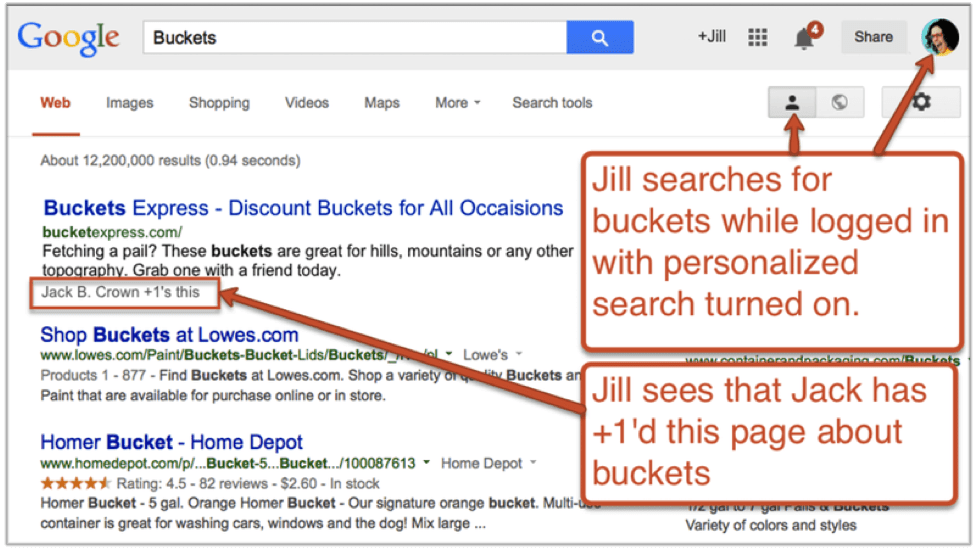
Naturally, activity in other social networks such as Facebook and Twitter do not affect Google search results, and Google+ activity does not affect Bing/Yahoo search rankings. But this has a direct impact on search rankings through social activity.
Rank is Driven by Links… A Link is a Social Thing
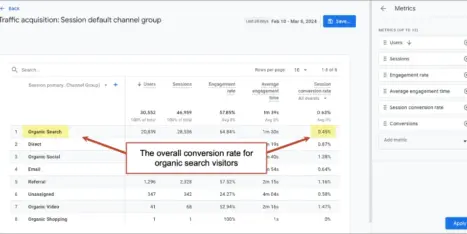
Here’s another clue into the importance of social activity to rankings: Google considers linking to be social activity. There is a report in your Analytics that shows new links to your site. You can find it under Acquisition > Social > Trackbacks. Here’s what it looks like.
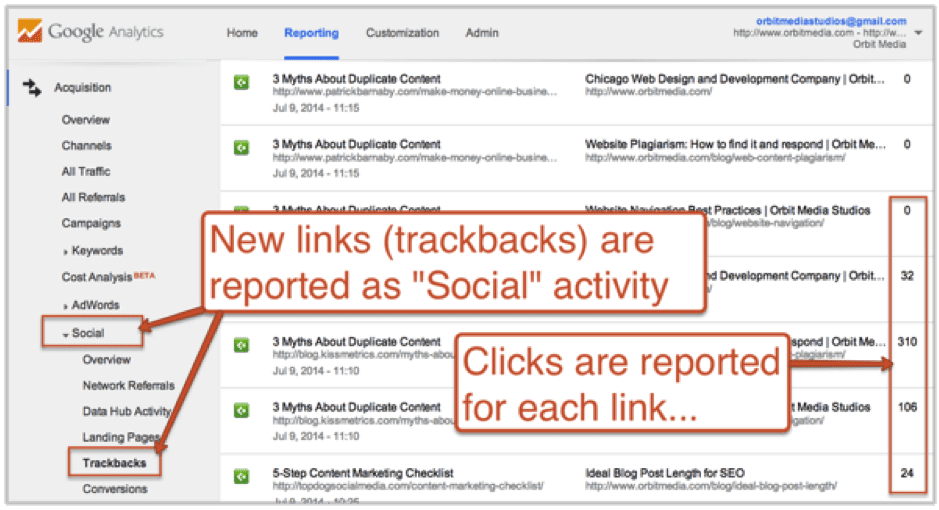
Not only does Google consider linking to be a social action, they report on how many times the link was clicked. This is another clue (or perhaps warning) that all links should be created with humans in mind. Yes, links cause sites to rank higher. But any link created purely for SEO reasons is spam. It is an attempt to artificially manipulate rankings.
Leveraging Indirect Benefits
If you watched me work for an hour, you’d think I was crazy. “How could THAT possibly help you sell websites in Chicago?” or “Why would that help you rank for a web design phrase?”
Rankings are an outcome, not an action. The great search optimizers are very active in social media because they understand the importance of indirect benefits.
Every aspect of modern marketing is based on relationships. Including search.
And relationships are built on social media.
I’ll leave you with a brilliant bit of insight from Sonia Simone of Copyblogger, “Google is a mean high school girl.” You can get her to like you but not by approaching her directly. You have to get everyone else to like you first…
For additional information, you should watch How Links Work in Google.